Imagine describing a delicious pizza. Adjectives are the words that give life to your description. They tell you what the pizza looks, tastes, and smells like. In simple terms, adjectives are words that modify or describe nouns.
Chances are, you’ve come across sentences like these:
- Mr. Smith is a kind person.
- Emma is a beautiful girl.
- They have a big house.
- It was a funny movie.
See those words—kind, beautiful, big, funny? They’re the secret sauce of sentences. They’re called adjectives. They make everyday nouns pop with extra meaning. Like how ‘kind’ describes Mr. Smith, ‘beautiful’ makes Emma shine, ‘big’ tells us about their house, and ‘funny’ adds a twist to the movie.
But wait, there’s more to this word magic! Let’s explore adjectives and types of adjectives with some cool examples.
What is an Adjective?
Adjective Definition: An adjective is a word that belongs to the parts of speech and modifies or describes a noun by providing more information about it. Adjectives add detail, color, and depth to sentences, enabling us to create more vivid and engaging descriptions. Examples of adjectives include nice, smart, wonderful, interesting, big, small, green, and red. Without adjectives, sentences can feel a bit plain. Check out this example:
- Plain: “She wore a dress.”
- With Adjective: “She wore a vibrant dress.”
An adjective usually comes BEFORE a noun to modify the noun. For example, She was wearing a green dress. Here “green” is an adjective that came BEFORE the noun “dress” to describe it.
However, sometimes an adjective can modify a pronoun as well. For example, I bought some new dresses yesterday. All of them are red. Here “red” is an adjective that modifies or describes the pronoun “them”.
Adjective Examples
The highlighted words in the sentences below are Adjective Examples.
- This a fascinating book about history.
- We recently traveled to a hill station which was an amazing experience.
- She doesn’t like to wear sleeveless dresses.
- I have an incredible idea for a new business.
- These are fresh and lovely flowers.
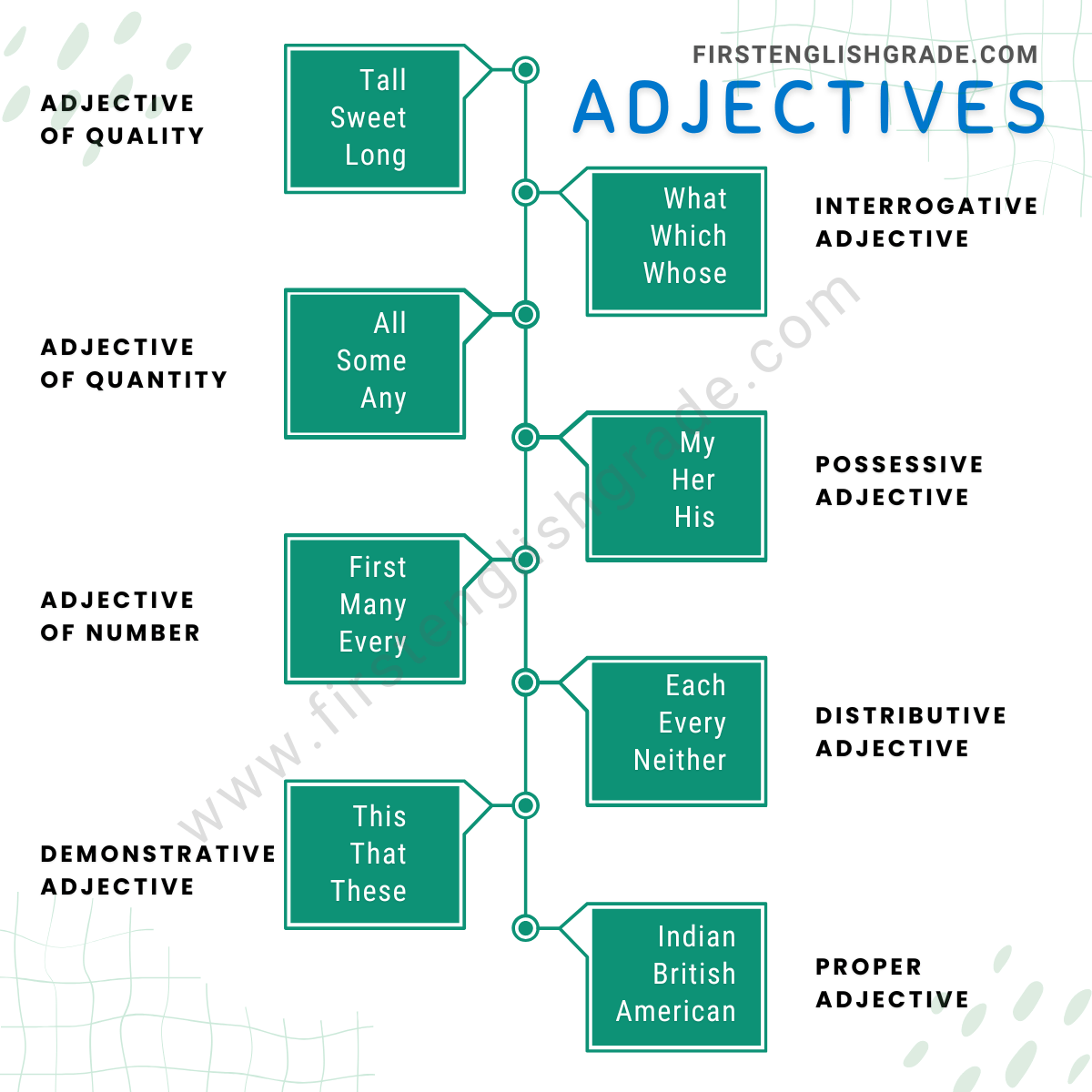
Types of Adjectives
There are different types of adjectives in English grammar.
Types of adjectives are:
- Adjective of Quality
- Adjective of Quantity
- Adjective of Number
- Demonstrative Adjective
- Interrogative Adjective
- Possessive Adjective
- Distributive Adjective
- Proper Adjective
- Exclamatory Adjectives
- Compound Adjectives
- Comparative Adjectives
- Superlative Adjectives
Types of Adjectives – Definitions and Examples
1. Adjective of Quality
A word that describes a noun’s quality, condition, or color is known as an adjective of quality. They help us understand the specific attributes of the noun.
Look at the below sentences:
- Jack is a tall, healthy man.
- Emily is a sweet girl.
- She has long brown hair.
The words tall, healthy, sweet, brown, and long are adjectives of quality.
Adjective of Quality Examples
Quality adjectives describe the shape, size, quality, state, color, etc., of a person or thing in a specific way.
Here are some examples of adjectives of quality
- Quality: interesting, amazing, difficult, true, false, etc.
- Color: black, blue, red, green, yellow, etc.
- Condition/state: happy, sad, strong, weak, old, healthy, fresh, etc.
- Size: tall, big, small, long, short, thin, thick, etc.
- Shape: square, round, flat, etc.
2. Adjective of Quantity
An adjective that indicates or conveys information about the quantity of a noun is called an adjective of quantity. Words such as some, all, much, more, enough, and little are examples of adjectives of quantity.
Adjective of Quantity Examples
- I need some information.
- They have enough food for the next two months.
- Do you have any idea about this problem?
- All students must submit their projects before Monday.
- He needs more money to continue his research.
3. Adjective of Number
Adjectives of numbers are used to indicate the quantity, order, or position of nouns. They provide a sense of numerical information, helping us understand how nouns relate to numbers.
Adjective of Number Examples
An adjective of number comes before countable nouns such as book, prize, friend, person, etc.
Look at the below sentences:
- I have two books in my bag.
- Jack won the first prize in the contest.
- She has many friends.
- I know every person sitting in this room.
The highlighted words two, first, many, and every, in the above sentences provide a sense of number or order. These are called Adjectives of Numbers.
4. Demonstrative Adjectives
Demonstrative adjectives point out specific nouns and help us identify which ones we’re referring to. “This book is fantastic.” – In this sentence, “this” points to a specific book, distinguishing it from other books. Demonstrative adjective examples are this, that, these, and those.
If you have studied pronouns, you probably already know that “this, that, these, and those” are also demonstrative pronouns. However, there is a difference between demonstrative pronouns and demonstrative adjectives.
Look at the sentences below…
- This girl is brilliant.
- That boy is my nephew.
- These clothes are dirty.
- Tell those students to go home.
As you can see from these examples, this, that, these, and those point to nouns.
If there is a noun after this, that, these, and those in a sentence, they are called demonstrative adjectives. Alternatively, if a noun does not appear immediately after this, that, these, and those, they are called demonstrative pronouns.
- This is an exciting book.
- These are my school friends.
Here, this and these are demonstrative pronouns because there is a verb (is/are) after them.
An easy way to identify Demonstrative Adjectives is:
This/that/these/those + NOUN = Demonstrative Adjective
5. Interrogative Adjectives
Interrogative adjectives help us ask questions about nouns. “Which movie are we watching tonight?” – In this question, “which” is an interrogative adjective that asks about a specific movie.
Interrogative Adjective Examples
- What options do I have now?
- Which restaurant serves the best meal?
- Whose shoes are these?
There is a noun in these questions, and before that, we have the words what, which, and whose. These question words serve as interrogative adjectives in these sentences. In a question sentence, if there is no noun immediately after the words what, which, and whose, they are called interrogative pronouns.
Examples
- What are the best career options?
- Which is your favorite movie?
- Whose are these books?
Here, what, which, and whose are all interrogative pronouns, as no noun follows them immediately in these sentences.
An easy way to identify Interrogative Adjectives is
What/which/whose + NOUN + …….? = Interrogative Adjective
6. Possessive Adjectives
As the name suggests, possessive adjectives are words used with a noun to indicate someone’s ownership or relationship with it. In other words, we use a possessive adjective to show that something belongs to someone. Possessive adjective examples are my, your, our, his, her, its, and their.
- My brother serves in the military.
- Currently, she is staying with her uncle.
- We are not planning on selling our house anytime soon.
- He has a scar on his neck.
- After walking for an hour, I could not feel my legs.
7. Distributive Adjectives
An adjective that refers to each person or thing in a group is called a distributive adjective. For example, neither computer in this lab is working. This sentence uses the distributive adjective “neither,” which refers to or specifies each computer individually. Distributive adjective examples are each, every, neither, and either.
- Each person in this room is above 18 years.
- Make sure every student has access to the library.
- He leaves the office early every day.
8. Proper Adjectives
Proper adjectives are derived from proper nouns (names of people, places, etc.) and describe characteristics related to them. “She admired the Italian architecture.” – In this sentence, “Italian” is a proper adjective derived from the proper noun “Italy.”
- Mr. William is an American citizen.
- Tom holds a British passport.
- Some Indian students attend this school.
American, British, and Indian are proper adjectives derived from the proper nouns America, Britain, and India. Some Proper Adjective Examples are – French, English, Japanese, Pakistani, and African.
9. Exclamatory Adjectives
Exclamatory adjectives are a type of adjectives used to convey strong emotions, feelings, or reactions. They are often found in sentences that express surprise, excitement, admiration, or other intense emotions.
Here are some examples of exclamatory adjectives:
- How amazing that performance was!
- Here, “amazing” is the exclamatory adjective. It shows the speaker’s strong sense of awe and astonishment towards the performance.
- What an incredible achievement!
- In this example, “incredible” is the exclamatory adjective. It conveys the speaker’s amazement and surprise at the achievement.
- What a fantastic job you’ve done!
- The exclamatory adjective “fantastic” indicates the speaker’s high level of approval and appreciation for the job done.
10. Compound Adjectives
Compound adjectives are adjectives that are formed by combining two or more words together to describe a noun. These combinations create a single adjective that provides more detailed information about the noun’s characteristics. Compound adjectives are hyphenated when they appear before a noun they modify.
Here are some examples of compound adjectives:
- Blue-eyed girl: Here, “blue-eyed” is a compound adjective that describes the girl. It tells us that the girl has blue eyes.
- Well-known author: “Well-known” is a compound adjective describing the author. It indicates that the author is widely recognized or famous.
- Two-story house: “Two-story” is a compound adjective that describes the house. It tells us that the house has two levels or floors.
- High-tech gadgets: “High-tech” is a compound adjective describing the gadgets. It suggests that the gadgets incorporate advanced technology.
- Open-minded person: “Open-minded” is a compound adjective describing the person. It suggests that the person is receptive to new ideas and perspectives.
11. Comparative Adjectives
Comparative adjectives are used to compare two or more nouns, indicating a higher or lower degree of the described quality. This degree is usually formed by adding “-er” to the end of the adjective or by using “more” before the adjective. Examples: bigger, smaller, faster, more vibrant, and cheaper.
Examples:
- Her painting is more vibrant than mine.
- This book is cheaper than the one I bought last week.
- The police couldn’t catch the thief because he was faster than them.
12. Superlative Adjectives
Superlative adjectives are used to express the highest degree of quality in relation to three or more nouns. This degree is often formed by adding “-est” to the end of the adjective or by using “most” before the adjective. Examples: biggest, smallest, tallest, most talented, and best.
Examples:
- This is the tallest building in my city.
- Everyone knows that she is the most talented singer in the choir.
- This is the best movie I’ve ever watched.
Order of Adjectives: Structuring Your Sentences
When using multiple adjectives to describe a single noun, English follows a specific order to maintain clarity and natural flow in sentences. This order is not strict in all cases, but it generally follows a pattern to ensure effective communication. The typical order of adjectives in a sentence is as follows:
- Opinion: This describes the speaker’s opinion or feelings about the noun.
- Size: This refers to the physical dimensions of the noun.
- Age: This indicates how old the noun is.
- Shape: This describes the physical shape of the noun.
- Color: This refers to the color of the noun.
- Origin: This tells us where the noun comes from.
- Material: This indicates what the noun is made of.
- Purpose: This describes the intended use or purpose of the noun.
Here’s a sentence that includes all these types of adjectives in the correct order:
Example: She bought a lovely (opinion) small (size) old (age) round (shape) red (color) Italian (origin) wooden (material) dining (purpose) table.
Explanation with Examples:
- Opinion: Lovely
- Size: Small
- Age: Old
- Shape: Round
- Color: Red
- Origin: Italian
- Material: Wooden
- Purpose: Dining
If we rearrange the adjectives randomly, the sentence becomes less clear:
- She bought a wooden red small Italian old round lovely dining table.
Notice how the original order creates a smoother flow and clearer image of the noun being described.
Adjectives vs. Adverbs
Both adjectives and adverbs play essential roles in modifying words in a sentence, but they serve different purposes and are used in distinct ways.
One way to distinguish between adjectives and adverbs is to consider what they modify. Adjectives modify nouns or pronouns, while adverbs modify verbs, adjectives, or other adverbs. Additionally, adverbs often end in “-ly,” although this is not a strict rule.
Examples:
- She wore a beautiful dress. (Adjective modifying the noun “dress”)
- She sang beautifully. (Adverb modifying the verb “sang”)
- He is a fast runner. (Adjective modifying the noun “runner”)
- He runs fast. (Adverb modifying the verb “runs”)
- The movie was very exciting. (Adverb modifying the adjective “exciting”)
- They arrived very early. (Adverb modifying the adverb “early”)
Understanding the distinction between adjectives and adverbs is crucial for constructing accurate and clear sentences. Adjectives enhance our understanding of nouns, while adverbs provide more context to verbs, adjectives, or other adverbs, enriching the overall meaning of the sentence.
Frequently Asked Questions (FAQ) about Adjectives
Q1: What is the role of adjectives in a sentence?
Adjectives modify nouns or pronouns, providing additional information about their attributes, qualities, or characteristics. They help paint a clearer picture of the nouns they describe.
Q2: How do adjectives differ from adverbs?
Adjectives modify nouns or pronouns, whereas adverbs modify verbs, adjectives, or other adverbs. Adjectives answer questions like “What kind?” or “Which one?”, while adverbs answer questions about how, when, where, or to what degree an action is performed.
Q3: What is the order of adjectives in a sentence?
Adjectives usually appear in a specific order to maintain clarity and natural flow: determiners/observations, opinion, size, shape, age, color, origin, material, and purpose/qualifier. Not all categories are necessary, and the order may vary based on context.
Q4: Can adjectives appear before and after nouns?
Yes, adjectives can be placed both before and after nouns. However, their position might affect the meaning or emphasis of the sentence. Adjectives are often hyphenated when they appear before nouns.
Q5: How are comparative and superlative degrees used with adjectives?
Comparative degrees compare two nouns, indicating higher or lower intensity. Superlative degrees compare three or more nouns, expressing the highest or lowest intensity. Comparatives are often formed by adding “-er” or using “more,” while superlatives use “-est” or “most.”
Q6: What are some common types of adjectives?
There are several types of adjectives, including descriptive, quantitative, demonstrative, possessive, interrogative, numeral, exclamatory, and compound adjectives.
Q7: Is the order of adjectives the same in all languages?
The order of adjectives may vary slightly across languages, but many languages follow a similar pattern to ensure clear communication and comprehension.